
#CISCO MAC ADDRESS TABLE 消去 MAC#
Switch(config-)# no mac-address-table static mac_address vlan vlan-idĭeletes the static entry from the MAC address table.
#CISCO MAC ADDRESS TABLE 消去 UPDATE#
If you enable the auto-learn option, the switch will update the entry if the same MAC address is seen on a different port. Specifies a static address to add to the MAC address table. switch(config-)# mac-address-table static mac_address vlan vlan-id You can also configure a static MAC address in interface configuration mode or VLAN configuration mode.Ģ. These addresses are static MAC addresses. You can configure MAC addresses for the switch. The switch uses an aging mechanism, defined by a configurable aging timer, so if an address remains inactive for a specified number of seconds, it is removed from the address table. The address table can store a number of unicast and multicast address entries without flooding any frames. A multicast address can accept more than one interface as its destination. In addition, you can enter a multicast address as a statically configured MAC address. These static MAC entries are retained across a reboot of the switch. You can also enter a MAC address, which is termed a static MAC address, into the table. The switch then forwards subsequent frames to a single LAN port without flooding all LAN ports. When the destination station replies, the switch adds its relevant MAC source address and port ID to the address table. When the switch receives a frame for a MAC destination address not listed in its address table, it floods the frame to all LAN ports of the same VLAN except the port that received the frame. The switch dynamically builds the address table by using the MAC source address of the frames received. When the switch receives a frame, it associates the media access control (MAcC) address of the sending network device with the LAN port on which it was received. If you are making a lot of changes you could also run the command clear arp-cache to clear the entire table.To switch frames between LAN ports, the switch maintains an address table. If you attempt to ping you device again you should find everything is fine and if you run the show command again you should see the entry in the ARP table now has the new MAC address Internet 10.24.100.54 1 912 ARPA Vlan124 Notice that the MAC address stored is still the original deviceĮnter the below command to clear this single dynamic entry clear ip arp 10.24.100.54

Resolution:ġ) Get yourself into the enable mode on the Cisco switch the device is connected to.Ģ) Enter the below command to see the entry in the ARP table for the IP 10.24.100.54.
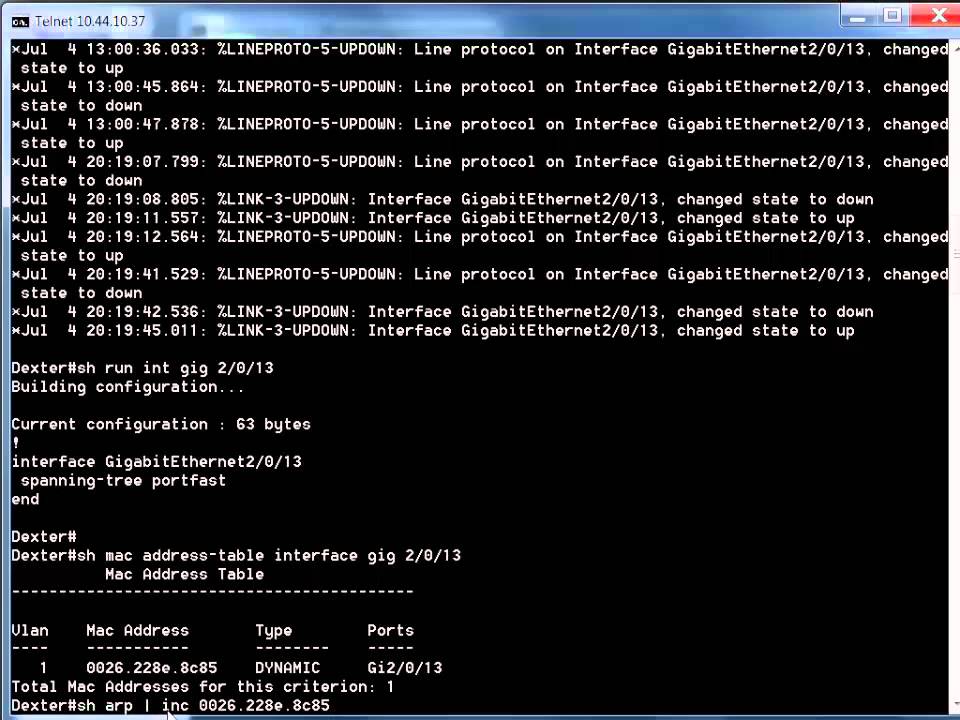
I have replaced a failed printer which has the IP 10.24.100.54 and the MAC address 00:80:77:b6:b:207 with a hot spare printer that has been setup to have the same IP 10.24.100.54 however its MAC address is 00:80:77:82:d9:12, the printer is all connected and configured fine however I am unable to ping or print. If you replace a device with another device that is still using the same IP address as the original device but has a different MAC address you find that you are unable to connect to it due to the ARP record on your Cisco device is still pointing to the original devices MAC address. If you are new to Cisco or just want to improve your skills I recommend this course from Udemy at the time of writing for just $20 for lifetime access! I’m also a really big fan of Pluralsight Problem: clear mac-address-table To remove a specified address (or set of addresses) from the MAC address table, use the clear mac-address-table command in privileged EXEC mode.

The ARP table on a Cisco device is a list of learned IP address and what MAC addresses they resolve to, this is required as generally switches work at layer 2 with MAC addresses not IP Address’s. This chapter presents the Cisco IOS LAN Switching and Multilayer Switching commands.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
